npj:金属薄膜在不同欠电位条件下如何实现超稳定?

海归学者发起的公益学术平台
分享信息,整合资源
交流学术,偶尔风月

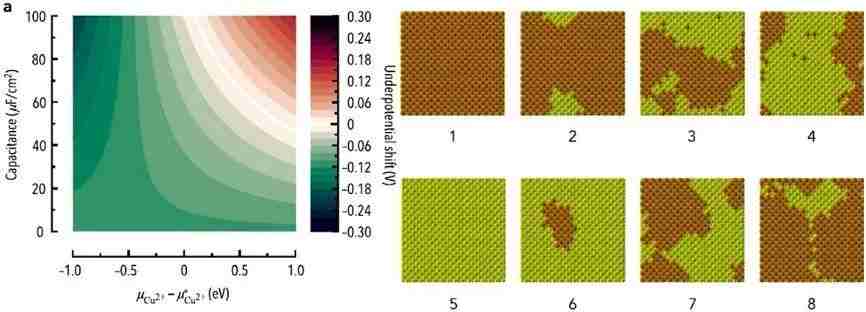
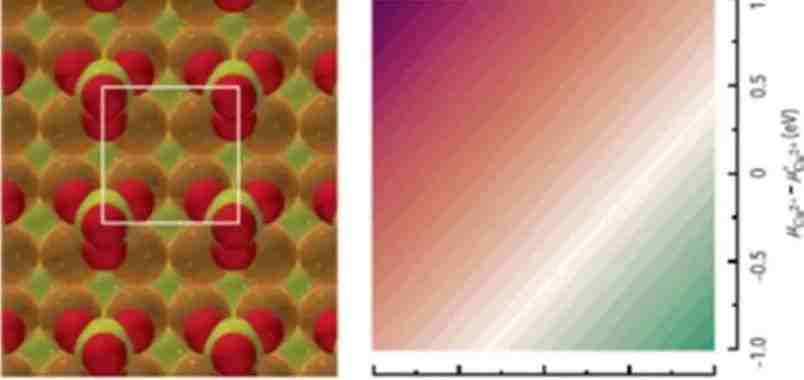
金属离子在欠电位条件下沉积到惰性金属材料表面,形成一层可用来催化或传感的纳米膜层。但这个方法所沉积的金属层不稳定,容易被周围的液体所溶解。采用量子力学模拟以找到最佳沉积方法的努力,因不能克服计算的不稳定性,而效果不佳。对此,来自美国宾州大学的Stephen Weitzner和Ismaila Dabo研发了一种新的模拟方法:用量子-连续体模型解释溶剂效应,用蒙特卡洛模拟阐述金-水界面的带电状况对沉积的影响。这样可以估计欠电位沉积时,铜离子在金表面的稳定性。他们的计算结果显示,要精确模拟欠电位的沉积,必须考虑界面电荷和共吸附离子等因素的影响。
论文近日发表于npj Computational Materials,文末“阅读原文”可以自由下载论文PDF。其标题与摘要如下:
Quantum–continuum simulation of underpotential deposition at electrified metal–solution interfaces
Stephen E.Weitzner & Ismaila Dabo
The underpotential deposition of transition metal ions is a critical step in many electrosynthetic approaches. While underpotential deposition has been intensively studied at the atomic level, first-principles calculations in vacuum can strongly underestimate the stability of underpotentially deposited metals. It has been shown recently that the consideration of coadsorbed anions can deliver more reliable descriptions of underpotential deposition reactions; however, the influence of additional key environmental factors such as the electrification of the interface under applied voltage and the activities of the ions insolution have yet to be investigated. In this work, copper underpotential deposition on gold is studied under realistic electrochemical conditions using aquantum–continuum model of the electrochemical interface. We report here on the influence of surface electrification,concentration effects, and anion coadsorption on the stability of the copper underpotential deposition layer on the gold (100) surface.
打开原文链接:
http://www.nature.com/articles/s41524-016-0004-9
或 点击文末“阅读原文”可以自由下载论文PDF。
欢迎广大学者供稿,报道最新研究成果 投稿、授权、合作事宜请联系
投稿、授权、合作事宜请联系

[email protected] 或微信ID: scholarset
回复“目录”或“分类”,浏览知社更多精华。长按二维码识别,可以关注/进入公众号进行回复。
最新评论
推荐文章
作者最新文章
你可能感兴趣的文章
Copyright Disclaimer: The copyright of contents (including texts, images, videos and audios) posted above belong to the User who shared or the third-party website which the User shared from. If you found your copyright have been infringed, please send a DMCA takedown notice to [email protected]. For more detail of the source, please click on the button "Read Original Post" below. For other communications, please send to [email protected].
版权声明:以上内容为用户推荐收藏至CareerEngine平台,其内容(含文字、图片、视频、音频等)及知识版权均属用户或用户转发自的第三方网站,如涉嫌侵权,请通知[email protected]进行信息删除。如需查看信息来源,请点击“查看原文”。如需洽谈其它事宜,请联系[email protected]。
版权声明:以上内容为用户推荐收藏至CareerEngine平台,其内容(含文字、图片、视频、音频等)及知识版权均属用户或用户转发自的第三方网站,如涉嫌侵权,请通知[email protected]进行信息删除。如需查看信息来源,请点击“查看原文”。如需洽谈其它事宜,请联系[email protected]。