Npj Comput. Mater.:薄至纳米级别,铪基薄膜的超强铁电性能研究进展
海归学者发起的公益学术平台
分享信息,整合资源
交流学术,偶尔风月
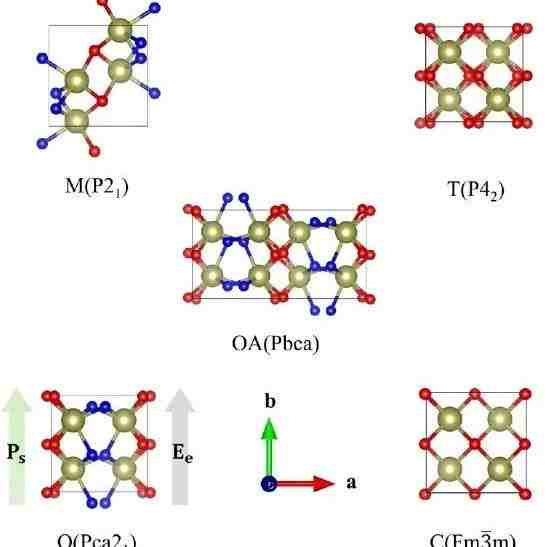
Fig. 1 Crystal structures of hafnia.
尽管铪基薄膜的铁电性前景光明,但其铁电性的源头却不甚明了。现代研究普遍认为,这种性质源自于空间群Pca21相(O相),然而O相在自然状态下并不稳定。为此,科研工作者努力寻找能够稳定O相的关键因素。在过去十年的研究中,掺杂剂和氧空位(VO)被证实对铪基薄膜的铁电性有着显著的影响,高离子半径和低电负性的掺杂剂,尤其是正三价掺杂剂,被发现对铁电相的形成尤为有利。此外,应力也被认为是影响铪基薄膜铁电性的一个关键因素。二维的平面压缩应力被认为有利于O相的形成,而外部的表面压缩应力则影响薄膜的剩余极化和疲劳效应。这种现象凸显了限制效应在铁电性中的重要性,与钙钛矿材料不同,揭示了铪基薄膜独特的尺寸效应。
Fig. 2 Effect of charged VO on
crystals.
最近,外加电场(Ee)对于铪基薄膜“唤醒”和疲劳效应的调控作用也得到了实验验证,指出电场能促使反铁电相(OA相)转变为O相。尽管单一因素已被证实可以促进O相的形成,但它们通常不能独立稳定O相,或需要在较为苛刻的条件下才能生效。因此,综合多种因素的联合作用,可能是稳定O相、进而开发具有优异铁电性能铪基薄膜的更可行之路。这一复合路径不仅提升了对条件的可达性,同时也为未来的铪基薄膜研究和应用提供了更为丰富的视角和可能性。
Fig. 3 Effects of uniaxial strain and VO coupling on crystal energies.
来自广东工业大学物理与光电工程学院蒋艳平副教授和西安电子科技大学周益春教授领导的团队,系统研究了氧空位(VO)、单轴应变和外部电场(Ee)对铪基晶体能量的单独及耦合影响。研究发现,虽然增加VO的数量能减少铁电相和单斜相之间的能量差距,但它并不能单独确保铁电相成为最稳定的形态。由于自发极化(Ps)与VO的浓度和电荷状态密切相关,这一现象揭示了VO与Ee之间的耦合作用。当氧空位与单轴应变共同作用时,单轴应变可独立稳定反铁电相,并提升铁电相的稳定性。同时,VO浓度和电荷状态的提升可以减少为稳定铁电相所需的应变。此外,单轴压缩应变能够提高铁电相的Ps,从而增强外部电场对相稳定性的影响力。
Fig. 4 Effect of
mechanical-electrical-chemical coupling on crystal energies.
这些发现指出,在铪基材料中铁电相的稳定是一个典型的机械-电-化学耦合过程。当同时考虑氧空位、单轴应变和外部电场时,能够更容易地实现铁电相的稳定。该研究为解释铪基材料中的“唤醒”现象提供了新的解释,并为实现及维持铪基材料中的铁电相提供了理论指导。
Fig. 5 Phase diagram of HZO.
该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 9:219(2023),英文标题与摘要如下,点击左下角“阅读原文”可以自由获取论文PDF。
Mechanical-electrical-chemical coupling study on the stabilization of a hafnia-based ferroelectric phase
Fenyun Bai, Jiajia Liao, Jiangheng Yang, Yanping Jiang, Xingui Tang, Qiuxiang Liu, Zhenhua Tang & Yichun Zhou
The metastable polar orthorhombic phase is believed to be the origin of the ferroelectricity of hafnia-based films. The adjustment of stain, oxygen vacancies and dopant during film deposition and the wake-up electric cycling are common strategies to induce the ferroelectricity in hafnia. However, none of them could independently render the ferroelectric phase to be the most stable phase from the theoretical calculation results. The exact external conditions to stabilize orthorhombic phase still remain elusive. In this paper, we investigate the effects of the type, distribution, concentration, and charge state characteristics of oxygen vacancies and the uniaxial strain on the crystal’ energy, dielectric constant and spontaneous polarization (Ps); In addition, the impact of the applied electric field parallel to the Ps on the crystal’ energy is explored by first-principles calculations. It is challenging to independently stabilize the ferroelectric phase of hafnia-based films by a single component owing to the rather strict conditions. Surprisingly, the ferroelectricity can be easily obtained when simultaneously considering the effects of oxygen vacancies, uniaxial strain, and applied electric fields, suggesting the extremely important mechanical-electrical-chemical coupling effects. This work provides an explanation for the typical wake-up phenomenon in hafnia and a guidance for film applications.
扩展阅读
媒体转载联系授权请看下方
关键词
效应
Npj Comput.Mater
电场
铁电性
氧空位
最新评论
推荐文章
作者最新文章
你可能感兴趣的文章
Copyright Disclaimer: The copyright of contents (including texts, images, videos and audios) posted above belong to the User who shared or the third-party website which the User shared from. If you found your copyright have been infringed, please send a DMCA takedown notice to [email protected]. For more detail of the source, please click on the button "Read Original Post" below. For other communications, please send to [email protected].
版权声明:以上内容为用户推荐收藏至CareerEngine平台,其内容(含文字、图片、视频、音频等)及知识版权均属用户或用户转发自的第三方网站,如涉嫌侵权,请通知[email protected]进行信息删除。如需查看信息来源,请点击“查看原文”。如需洽谈其它事宜,请联系[email protected]。
版权声明:以上内容为用户推荐收藏至CareerEngine平台,其内容(含文字、图片、视频、音频等)及知识版权均属用户或用户转发自的第三方网站,如涉嫌侵权,请通知[email protected]进行信息删除。如需查看信息来源,请点击“查看原文”。如需洽谈其它事宜,请联系[email protected]。